Antibiotic Injuctions Uses & Disadvantages
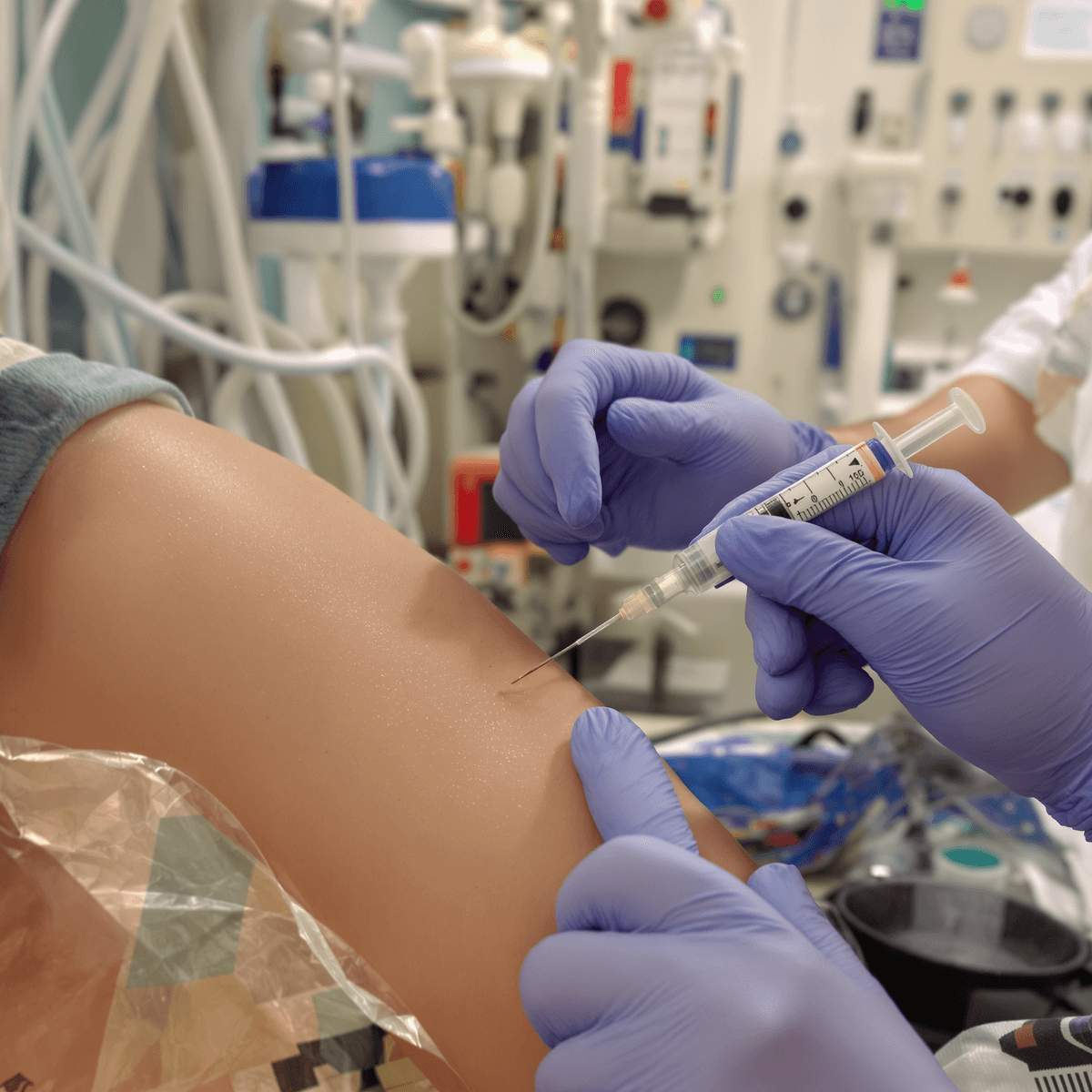
Antibiotic injections are a powerful medical treatment used to fight bacterial infections. They are given directly into the bloodstream or muscle tissue, allowing the medication to work quickly and effectively. These injections are especially useful for severe or life-threatening infections where immediate action is required.
Key Features of Antibiotic Injections:
- Rapid absorption into the bloodstream
- Higher concentration of medication delivery
- Bypass digestive system absorption
- Immediate therapeutic effect
- Controlled dosage administration
It's important for both healthcare providers and patients to understand when antibiotic injections are used and what their drawbacks may be. While these medications can save lives in certain situations, they also come with potential risks that need to be carefully considered. Knowing when these treatments are necessary - and when they might do more harm than good - can greatly influence your healthcare choices.
The effectiveness of antibiotic injections relies on proper administration, timely delivery, and close monitoring. Healthcare providers must assess each case individually, weighing the benefits against possible side effects. This careful approach ensures you receive the most suitable treatment while minimizing risks associated with injectable antibiotics.
1. Uses of Antibiotic Injections
These injectable medications deliver antibiotics directly into the bloodstream or muscle tissue, providing rapid and effective treatment when immediate action is required.
Primary Applications:
1. Severe Bacterial Infections
- Meningitis
- Blood infections (sepsis)
- Bone and joint infections
- Complicated respiratory infections
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
2. Post-Surgical Care
- Prevention of surgical site infections
- Treatment of existing surgical complications
- Prophylactic administration before high-risk procedures
3. Emergency Situations
- Rapid infection control
- Life-threatening bacterial conditions
- Cases requiring immediate antibiotic presence in bloodstream
Specific Medical Conditions:
Antibiotic injections are particularly effective in treating:
- Gonorrhea
- Deep tissue infections
- Complicated urinary tract infections
- Severe skin infections
- Abdominal infections
Alternative to Oral Antibiotics
Injectable antibiotics become necessary when:
- Patients cannot swallow medications
- Digestive system absorption is compromised
- Immediate high-concentration antibiotic levels are needed
- Oral antibiotics prove ineffective
- Severe vomiting prevents oral medication retention
Administration Methods:
- Intravenous (IV): Direct delivery into bloodstream, continuous administration possible, precise dosage control.
- Intramuscular (IM): Single-dose administration, slower release into bloodstream, suitable for outpatient treatment.

Treatment Settings:
- Hospital environments
- Outpatient clinics
- Home care (under medical supervision)
- Emergency departments
- Surgical facilities
Special Considerations:
Antibiotic injections require careful selection based on:
- Infection type and severity
- Bacterial strain identification
- Patient's medical history
- Previous antibiotic responses
- Potential drug interactions
Healthcare providers often choose injectable antibiotics for their ability to maintain consistent medication levels in the body. This delivery method bypasses common absorption issues associated with oral antibiotics, ensuring that the medication reaches its target site quickly and effectively.
2. Disadvantages and Side Effects
Antibiotic injections can trigger various side effects ranging from mild discomfort to severe medical complications. Understanding these potential risks helps patients make informed decisions about their treatment.
Local Injection Site Reactions
- Persistent pain lasting several hours to days
- Visible redness and swelling around the injection area
- Tenderness when touching or moving the affected area
- Warmth radiating from the injection site
- Temporary muscle stiffness
Allergic Reactions
- Mild symptoms such as skin rashes, itching, hives, or minor swelling
- Severe reactions (anaphylaxis) characterized by difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, drop in blood pressure, swelling of face/throat/tongue, or loss of consciousness
Gastrointestinal Complications
Certain antibiotics can cause gastrointestinal issues.
- Nausea and persistent vomiting
- Intense abdominal cramping
- Loss of appetite
It's important to note that these gastrointestinal complications are not uncommon with antibiotic use as highlighted in this study.

Systemic Side Effects
In some cases, antibiotic injections may lead to systemic side effects affecting the entire body. These may include:
- Fever spikes above 101°F (38.3°C)
- Recurring chills and sweating episodes
- Unexplained fatigue or tiredness
- Muscle weakness
- Joint pain or discomfort
Serious Complications
While rare, certain serious complications can arise from antibiotic injections. These include:
- Symptoms of pancreatitis such as upper abdominal pain, nausea, and elevated enzyme levels
- Medication interactions resulting in reduced effectiveness of birth control pills, interference with blood-thinning medications, or reactions with calcium-containing solutions
Medical Test Interference
Antibiotic injections have the potential to interfere with certain medical tests. Patients should be cautious of the following:
- False-positive results in diabetic urine glucose tests
- Altered blood test results (e.g., liver function tests)
- Inaccurate kidney function readings
- Type of antibiotic used
- Dosage administered
- Patient's medical history
- Individual sensitivity to medications
- Presence of underlying health conditions
3. Monitoring and Precautions for Patients Receiving Antibiotic Injections
Proper monitoring during antibiotic injection treatment plays a crucial role in patient safety and treatment effectiveness. Healthcare providers implement specific protocols to track patient responses and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Key Monitoring Requirements:
- Regular vital sign checks during and after administration
- Blood tests to assess kidney and liver function
- Periodic assessment of injection sites
- Documentation of any new symptoms or reactions
- Regular evaluation of treatment effectiveness
Essential Patient Responsibilities:
- Maintain a detailed medication list, including:
- Prescription medications
- Over-the-counter drugs
- Herbal supplements
- Vitamins and minerals
- Report any changes in health status promptly
- Track and document side effects
- Keep all scheduled follow-up appointments
Healthcare providers need accurate information about your medical history and current medications to prevent potentially dangerous drug interactions. Some medications, such as chlorpromazine hydrochloride, can alter the effectiveness of antibiotic injections or increase the risk of side effects.

Red Flags Requiring Immediate Reporting:
- Unusual heart rate changes
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe skin reactions
- Unexpected bleeding
- Changes in urination patterns
- Mental status changes
Your healthcare team might require you to maintain a treatment diary, recording:
- Time and date of each injection
- Any immediate reactions
- Changes in symptoms
- New side effects
- Temperature readings
- Pain levels
Regular communication with your healthcare provider ensures appropriate dosing adjustments and helps identify potential complications early. Some patients might need more frequent monitoring based on their medical history, age, or specific health conditions.
It's also important to note that certain health conditions may require more specialized care, which could involve additional education or training for both the patient and the healthcare provider. For instance, resources like the NCSBN's RN Test Plan can provide valuable insights into the nursing processes involved in such care scenarios.
4. Emergency Situations Related to Antibiotic Injections: Recognition and Treatment
Here are the critical signs of severe allergic reactions and overdose you need to watch for:
Signs of Severe Allergic Reactions:
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Swelling of face, throat, or tongue
- Rapid, weak pulse
- Severe dizziness
- Skin reactions (hives, rash spreading quickly)
- Loss of consciousness
Overdose Warning Signs:
- Seizures
- Severe stomach cramps
- Unusual bleeding
- Extreme fatigue
- Mental confusion
- Irregular heartbeat
Immediate Actions in Emergency Situations:
- Call Emergency Services (911) - Don't wait to see if symptoms improve
- Stop the Injection - If currently being administered
- Use Emergency Medications - Apply prescribed EpiPen if available for allergic reactions
- Position the Patient - Lay flat with legs elevated for shock
- Monitor Vital Signs - Track breathing, pulse, and consciousness levels
Hospital Treatment Protocols:
- Administration of epinephrine for anaphylaxis
- IV fluids to maintain blood pressure
- Oxygen therapy when needed
- Antihistamines and steroids for allergic reactions
- Specific antidotes for particular antibiotic overdoses
Risk Reduction Strategies:
- Start with test doses for new antibiotics
- Keep emergency medications readily available
- Wear medical alert jewelry if known allergies exist
- Maintain detailed records of reactions
- Learn to self-administer emergency medications if prescribed
Medical facilities administering antibiotic injections maintain emergency protocols and equipment for immediate intervention. Home-care patients receiving injections should have emergency response plans prepared by their healthcare providers.

Conclusion
Antibiotic injections are powerful tools in modern medicine, providing quick and effective treatment for severe bacterial infections. They are especially valuable in healthcare settings for preventing complications after surgery and treating infections that do not respond to oral medications.
However, the decision to use antibiotic injections should be made carefully, considering both the benefits and risks involved. While these medications can save lives, they also have potential side effects that can range from mild discomfort to severe allergic reactions. This is why it is crucial to have your healthcare provider's expertise in:
- Determining the right type and dosage of antibiotics for you
- Monitoring how you respond to the treatment
- Managing any potential side effects that may arise
- Making adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary
Remember: Each patient's medical history, current health status, and specific infection type create unique circumstances that require personalized medical attention. Never attempt to self-diagnose or self-administer antibiotic injections.
Here are some ways you can contribute:
- Stay informed about your medication: Take the time to learn about the antibiotics you are being prescribed, including their purpose, potential side effects, and any interactions with other medications or substances.
- Communicate openly with your healthcare team: If you have any concerns or experience any side effects during your treatment, make sure to communicate them promptly to your healthcare provider. This will help them address any issues and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Follow prescribed treatment protocols precisely: It is important to adhere strictly to the instructions given by your healthcare provider regarding when and how to take your antibiotic injections. This will ensure that the medication is effective in treating your infection.
If you experience unexpected reactions or have questions about your antibiotic injection treatment, do not hesitate to contact your healthcare provider immediately. Your health and safety are always the top priority throughout the treatment process.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the primary uses of antibiotic injections?
Antibiotic injections are primarily used to treat severe bacterial infections that require rapid and effective medication delivery. They are commonly administered to prevent or treat post-surgical infections, ensuring faster recovery and reduced complications. Additionally, they serve as a potent alternative when oral antibiotics are ineffective or not feasible.
What are the common disadvantages and side effects of antibiotic injections?
Common disadvantages include pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness at the injection site.Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and diarrhea can occur, along with other side effects like vomiting, stomach pain, fever, chills, and rare complications such as pancreatitis.
Why is monitoring important for patients receiving antibiotic injections?
Careful monitoring is essential to detect adverse reactions promptly in patients receiving antibiotic injections. It ensures timely management of side effects and prevents complications. Patients should inform healthcare providers about all medications they are taking to avoid harmful interactions.
Emergency situations include signs of overdose or severe allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing, swelling, or anaphylaxis. Immediate medical attention is critical in these cases. Prompt recognition and treatment can prevent serious health consequences.
When are antibiotic injections preferred over oral antibiotics?
Antibiotic injections are preferred when oral antibiotics are ineffective or not feasible, such as in severe infections requiring rapid action or when patients cannot tolerate oral medications. They provide direct and potent delivery of medication to combat infections effectively.
What precautions should patients take when receiving antibiotic injections?
They should report any side effects promptly and follow monitoring instructions carefully. Awareness of potential allergic reactions and gastrointestinal issues is important for safe use.
Thank you for visiiting my blog please share to your friends & family for encouraging me.
Nivas Cherry 🍒
cantact details :
email : nivascherry595@gmai.com
Post a Comment